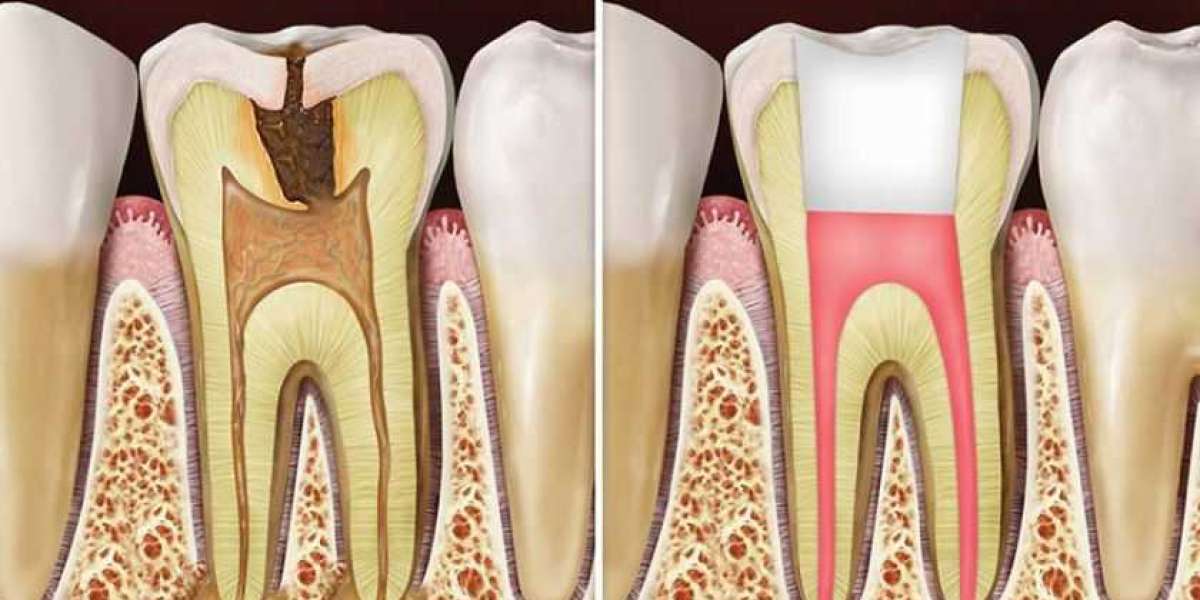
Introduction
Root canal treatment is a common dental procedure aimed at saving a severely infected or damaged tooth. While the procedure itself removes the infected pulp, antibiotics are often prescribed afterward to ensure complete elimination of bacteria and prevent potential post-treatment complications. Understanding The Role of Antibiotics After Root Canal care is crucial for both dental professionals and patients to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
After a root canal procedure, antibiotics play a significant role in preventing infection recurrence and promoting healing. These medications are prescribed to eliminate any remaining bacteria that may linger in the treated tooth or surrounding tissues. While the root canal itself removes the infected pulp, antibiotics target bacteria that may have spread beyond the tooth's roots.
Choosing the right antibiotic is essential in post-root canal care. Dentists typically prescribe antibiotics based on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient's medical history and any known allergies. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include amoxicillin, penicillin, and clindamycin. These medications work by either killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth, ultimately aiding in the body's natural healing process.
It's important for patients to follow their dentist's instructions regarding antibiotic usage diligently. This includes taking the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Failure to complete the antibiotic course can lead to antibiotic resistance, where bacteria become less responsive to treatment, posing a significant public health concern.
While antibiotics are effective in preventing infection after a root canal, they are not always necessary. In cases where the infection is localized and adequately treated during the procedure, antibiotics may not be required. However, for more complex cases or instances of systemic infection, antibiotics are crucial for preventing complications and promoting recovery.
Conclusion
Antibiotics play a vital role in post-root canal care by eliminating residual bacteria and preventing infection recurrence. Dentists carefully prescribe these medications based on the individual patient's needs and infection severity. Patients must adhere to their dentist's instructions regarding antibiotic usage to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance. By understanding the role of antibiotics in post-root canal care, both dental professionals and patients can contribute to successful treatment and long-term oral health.