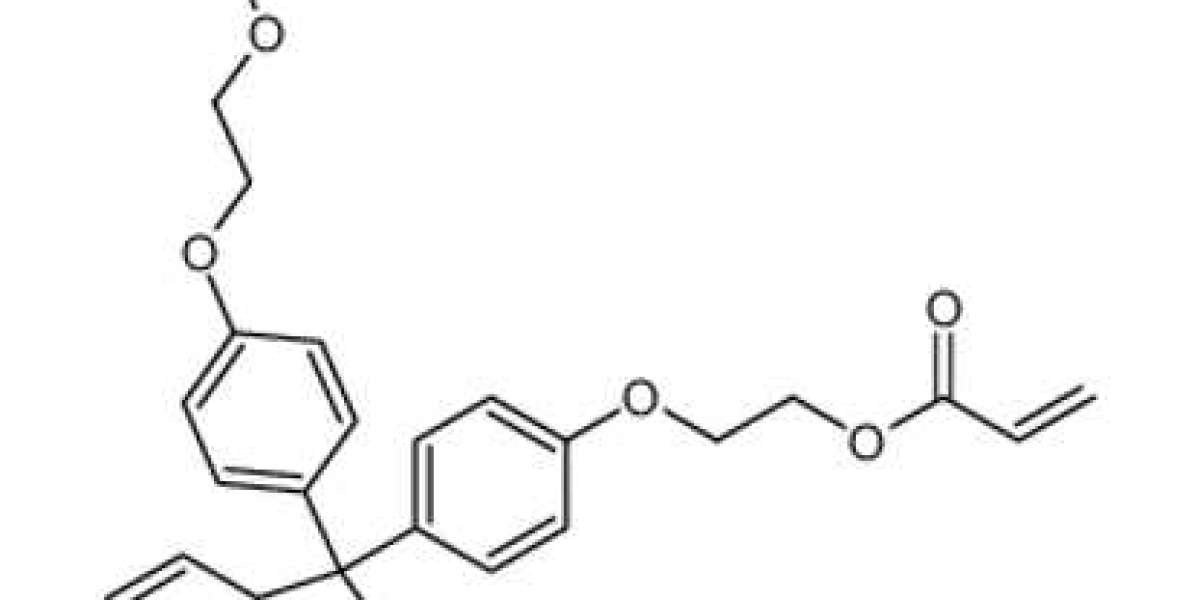
Impurity standards are critical for pharmaceutical analysis, ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of drug products. As the pharmaceutical industry evolves, so do the requirements for impurity standards. In this post, we'll explore the future of impurity standards, focusing on innovations and trends in supplier services shaping the landscape.
- Enhanced Purity and Characterization:
Future impurity standards will exhibit higher purity levels and comprehensive characterization. Suppliers will invest in advanced analytical techniques such as NMR, MS, and chromatography to provide impurity reference materials with well-defined structures and minimal impurities themselves.
- Certified Reference Materials (CRMs):
There will be a growing demand for CRMs with traceable and internationally recognized certification. Suppliers will adhere to strict quality standards, offering CRMs with documented accuracy, traceability, and metrological traceability according to regulatory requirements.
- Stable Isotope-Labeled Standards:
Stable isotope-labeled standards will gain prominence for quantitative analysis and pharmacokinetic studies. Suppliers will expand their offerings of labeled impurity standards, facilitating accurate quantification and metabolite identification in drug development.
- Custom Synthesis Services:
Suppliers will offer custom synthesis services for impurity standards tailored to specific customer needs. This will enable pharmaceutical companies to obtain impurity standards not commercially available, essential for method development and validation.
- Reference Libraries and Databases:
Comprehensive impurity reference libraries and databases will be developed by suppliers, containing spectral data, chromatograms, and purity information. These resources will aid in impurity identification, helping researchers to match and characterize impurities effectively.
- Stability-Indicating Impurity Standards:
With increasing regulatory scrutiny, there will be a focus on stability-indicating impurity standards. Suppliers will provide impurities that mimic degradation products, enabling thorough stability testing of pharmaceutical formulations.
- Online Platforms and Digital Solutions:
Suppliers will invest in user-friendly online platforms for easy browsing, purchasing, and accessing documentation for impurity standards. Digital solutions will streamline the ordering process and provide instant access to certificates and technical information.
- Quality Management Systems (QMS):
Implementation of robust QMS will be crucial for impurity standards suppliers to ensure consistency, traceability, and adherence to regulatory standards throughout the manufacturing process.
- Collaboration with Regulatory Bodies:
Suppliers will collaborate closely with regulatory bodies to align standards with evolving regulatory guidelines and pharmacopeial requirements, ensuring compliance and acceptance of impurity reference materials globally.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
Sustainability will become a key focus, with suppliers adopting eco-friendly practices in sourcing, manufacturing, and packaging of impurity standards to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion:
The future of impurity standards lies in innovation, quality, and adaptability to meet the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical industry. Suppliers will play a crucial role in providing high-quality, well-characterized impurity standards, supporting drug development, regulatory compliance, and ultimately, ensuring patient safety. Stay tuned for advancements that will shape the future of impurity standards in pharmaceutical analysis.