Overview
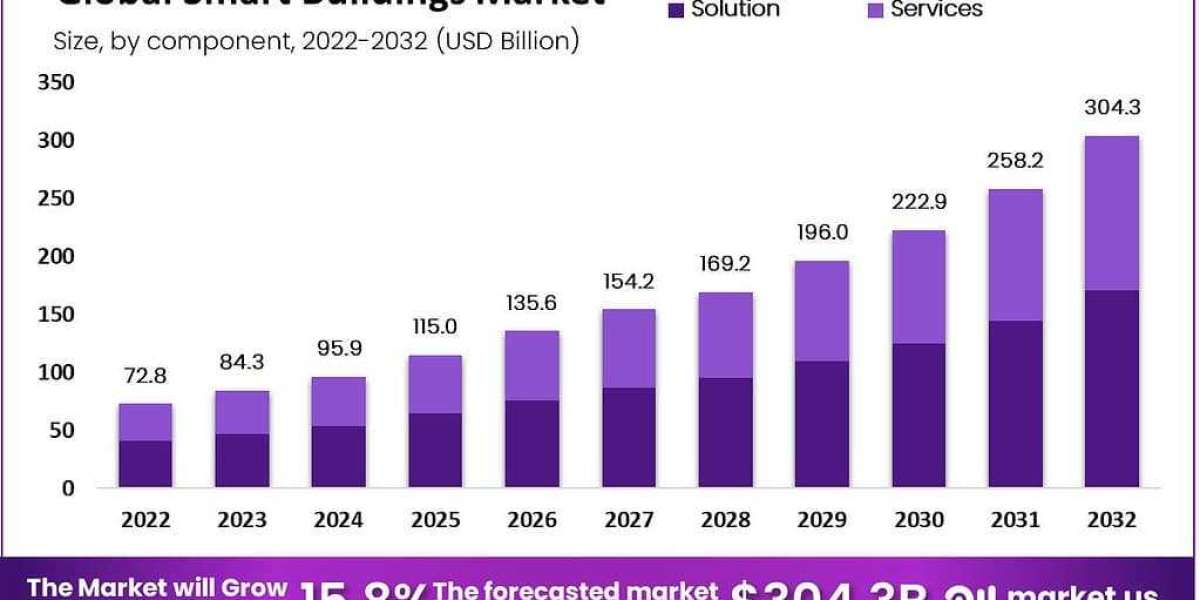
Global smart buildings market accounted for USD 72.8 billion and is expected to reach USD 304.3 billion in 2032, this market is estimated to register a CAGR of 15.8%.
The smart buildings market refers to the industry focused on integrating advanced technology into building systems to improve efficiency, comfort, and sustainability. Smart buildings use interconnected devices and sensors to automate and optimize functions like lighting, heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), security, and more. This technology allows buildings to respond intelligently to changing conditions, such as occupancy levels or weather patterns, to enhance the overall user experience and operational efficiency.
As a market research analyst, I observe that the smart buildings market is driven by several key factors. Firstly, there is a growing awareness of environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. Smart buildings can reduce energy consumption by adjusting systems based on real-time data, ultimately lowering operational costs and carbon footprints. Secondly, the demand for better occupant comfort and productivity is increasing. Smart technologies enable personalized control over lighting, temperature, and air quality, enhancing comfort and creating healthier indoor environments.
Furthermore, advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technology and cloud computing have significantly boosted the capabilities of smart building solutions. These technologies enable remote monitoring and control, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making, which are increasingly valued by building owners, facility managers, and tenants alike. As the market continues to evolve, smart buildings are expected to become standard practice in urban development, contributing to sustainable growth and improved quality of life.
Key Market Segments
Based on Component
- Solution
- Building Infrastructure Management
- Security and Emergency Management
- Energy Managementa
- Network Management
- Workforce Management
- Waste Management
- Services
- Consulting
- Implementation
- Support and Maintenance
Based on End-User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
Download a sample report in MINUTES@https://market.us/report/smart-building-market/request-sample/
The smart buildings market is segmented into solutions and services. The solution segment is the most profitable, with a projected CAGR of 15% and a total revenue share of 56% in 2022.
By end-user, the market is divided into commercial, residential, and industrial. The commercial segment is the most lucrative, holding a revenue share of 56.1% and a projected CAGR of 15% during the forecast period.
Key Players
- ABB Ltd.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Hitachi Ltd.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Johnson Controls
- Legrand SA
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Telit
- IBM Corporation
- Other Key Player
Driving Factors:Increasing demand for energy efficiency and urbanization are key drivers in the smart building market. Rising energy prices and environmental concerns emphasize energy-efficient buildings, which smart buildings achieve by optimizing energy consumption. Urban growth demands smart buildings that can efficiently accommodate large populations, optimize space, and enhance safety.
Opportunities:Advancements in IoT and AI technologies provide new opportunities for smart building automation. Sensors and devices collect data on building performance and user behavior, optimizing operations and improving comfort and safety. Growing awareness among building owners and operators about cost savings, enhanced occupant comfort, and sustainability drives investment in smart technologies.
Restraining Factors:Implementing smart building technologies requires specialized skills, and there may be a shortage of qualified professionals, hindering installation and maintenance. Reliance on data collection and communication makes smart buildings vulnerable to cyberattacks, raising security concerns. Resistance to change from building owners accustomed to traditional systems can also limit the adoption of smart technologies.
Challenges:Overcoming the skills gap and ensuring cybersecurity are major challenges. Convincing building owners of the profitability and benefits of smart technologies, despite their resistance to change, is crucial for broader market adoption.